
- Velvety patches in the mouth Patches are one of the most common symptoms of oral cancer. Patches can be white (leukoplakia), red and white (erythroleukoplakia), and red (erthryoplakia). Each patch color can become malignant, but red patches are most likely to be cancerous.
- Sores or lesions of the face, neck, mouth or lips We all get occasional sores on our mouths and lips, but cancerous sores are persistent and bleed often. If you have a sore on your mouth or lips for more than two weeks, contact your doctor immediately. Squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer, is the most common type of oral cancer, accounting for 90% of diagnosed cases. Squamous cell carcinomas grow on the surface of the mouth, and they usually appear as sores or ulcers with firm borders, which may frequently bleed.
- Lump on the lip, mouth, or throat or thickening of the cheek that can be felt with the tongue Lumps in the mouth are not unusual. Warts, bony growths, cysts, and even non-cancerous tumors are fairly common occurrences. Malignant tumors will typically be hard and immovable. Though most lumps in the mouth are usually benign, it is absolutely important that you get any and all lumps and bumps checked out by a doctor because your chance of recovery and survival is greater, the earlier cancer is detected.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing or difficulty moving the jaw or tongue. Not only is difficulty chewing or swallowing painful and often scary, it could be a sign of something more serious. Tumors might be lurking in places that are unable to feel or touch. Though 90% of all oral cancers are squamous cell carcinoma, there are two other kinds of oral cancer, verrucous carcinoma, and minor salivary gland cancers. Verrucous carcinoma is often known as snuff dipper cancer because this form of cancer is common among those who chew tobacco or use snuff. Salivary gland cancers are the most uncommon form of oral cancers, but there are a number of salivary glands in the mouth and it is possible, though not probably, to develop a number of different cancers in the salivary glands.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing or difficulty moving the jaw or tongue. Not only is difficulty chewing or swallowing painful and often scary, it could be a sign of something more serious. Tumors might be lurking in places that are unable to feel or touch. Though 90% of all oral cancers are squamous cell carcinoma, there are two other kinds of oral cancer, verrucous carcinoma, and minor salivary gland cancers. Verrucous carcinoma is often known as snuff dipper cancer because this form of cancer is common among those who chew tobacco or use snuff. Salivary gland cancers are the most uncommon form of oral cancers, but there are a number of salivary glands in the mouth and it is possible, though not probably, to develop a number of different cancers in the salivary glands.
- Swelling of the jaw
A special note to denture wearers: If your dentures begin to fit poorly or cause you discomfort, make an appointment to see your dentist. Keep in mind that the swelling of any tissue indicates an underlying problem. Like many of the other symptoms of oral cancer, the jaw can swell for a number of reasons like an infection or trauma.
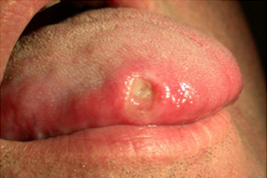
Other symptoms of oral cancer can include
- Unexplained numbness, sudden loss of feeling, or pain in the jaw, neck, or ear.
- Hoarseness, sore throat, or a change in the voice.
- Sudden and dramatic weight loss.